Hey guys. I am always eager to bring something new and informative to you. In this article, I am going to talk about Thematic Analysis. It is the most usable analysis for qualitative research. What is analysis? Why do we need analysis? These questions always derive, and that’s why I am here to solve all such questions for you.
Thematic analysis is a common form of Analysis. It focuses on emphasizing, recording and examining patterns within a data system. Themes are like patterns all over the databases that are important to the specification of a phenomenon.
These themes become the categories for analysis. Thematic analysis is done through the process of coding in six phases to build patterns which are meaningful and established.
Now, let’s learn in detail about Thematic analysis. In this article I will cover the following:
- What is Thematic Analysis?
- Advantages of Thematic Analysis.
- How to do a Thematic Analysis step by step?
- Disadvantages of Thematic Analysis.
So, let’s begin with the brief detailing. 🙂
1) What is Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is known to be the most commonly used method of analysis which gives you a qualitative research. It gives you an organized and richly described information regarding the database. It is beyond counting phrases or words in a text and it is something above that.
Coding is used to develop themes in the raw data. It recognizes crucial moments in the data and encodes it before interpretation. The explanation of the codes includes: comparing of theme frequencies, graphically displaying relationships within different themes and finding out theme co-occurrence.
There is a lot when it to it comes to a data set. Texts can vary from an open-ended question to a single word response or even a body of thousands of pages. Most qualitative researchers end up in-depth interviews which can last long for two hours, coming out to be nearly forty pages of transcribed data per respondent. But, the complexity depends on the type of data which you refer.
The thematic analysis holds onto the concept of supporting declaration with data from the grounded theory. It includes construction of theories that are grounded in the data themselves. This is reflective in this analysis as this process consists of identifying possible themes, reading transcripts, comparing and contrasting themes, etc.
Thematic analysis also relates with phenomenology. It gives importance to the participant’s perceptions, experiences and feelings as the major object of study. Phenomenology is rooted in humanistic psychology. It permits the respondents to discuss the topic in their own words, free of limitations.
This method of data analysis i.e., thematic analysis, can occur in two primary forms:
- Inductive approach- it includes the process of coding which occurs without trying to adjust the data into a pre-existing model or frame. This doesn’t mean that the researchers can get rid of their theoretical “epistemological responsibilities.”
- Deductive approach- this approach is more of theory-driven. It includes analysis, which is limited to preconceived frames. The result we get to focus on one or two aspects of the data that were determined by data analysis.
Then you have other forms as well which are as follows:
- Semantic way- It is believed that in this approach, coding and theme development displays the clear content of the data.
- Latent way- In this approach, coding and theme development details out the concepts and assumptions by grounding the data.
- Realist or Essentialist way- it gives attention on reporting a reality evident in the data which is assumed.
- Constructionist way- focuses on seeing that how a certain reality gets developed by the data.
Usage of Thematic Analysis in Psychology
Thematic Analysis is a widely used method within psychology. It offers theoretically flexible and an accessible approach towards obtaining a qualitative data. It is about different epistemological and ontological positions.
Thematic analysis becomes a part of psychology where you are guided with clarity on how to start a thematic analysis. Also, you get to learn to conduct it more rigorously and deliberately. You also consider potential pitfalls in organizing thematic analysis.
In psychological studies, you focus on the disadvantages and advantages of thematic analysis. Thematic Analysis is in and beyond psychology.
Thematic Analysis Example
It is a method for identifying semantic patterns in data. But, sometimes, it generates interpretative and sophisticated analyses that go beyond the obvious content.
There is an excellent example of Frith and Gleeson’s analysis in 2004. It was an analysis of 75 men’s views on their clothing styles and their bodies. They asked the men these three main questions:
- How does your thinking towards your body type, influence your clothing styles?
- Do you dress in a way that conceals the features of your body?
- Do you dress in a way that defines the features of your body?
Four different themes were identified under this survey. Two of the themes that were- “Men value functionalism” and “Men should not care regarding how they look”-portrayed a typical story of heterosexual men and clothing. At the same time, the other two themes- “Clothes are meant to hide or reveal” and “Clothes are meant to showcase culture”- spoke a more surprising story.
The results of this survey were that most of the men used clothing to change their looks according to the cultural ideals of masculinity. In the news, this survey was depicted as “body imaging,” an activity which deals with principals of social constructionism.
Frith and Gleeson’s work gives us a perfect example of how Thematic Analysis can be used to provide solid interpretations of data. It also includes a rework of theoretical concepts and to cook arguments.
2) Advantages Of Thematic Analysis
Researchers who conduct qualitative analysis, select the correct method to solve the research questions. An analysis should be based on both theoretical assumptions and the research questions. The thematic analysis gives you a flexible way of data analysis and permits researchers with different methodological backgrounds, to engage in such type of analysis.
let’s now look at the advantages:
- It provides a vast amount of flexibility. Many theories can be applied to this process across various range of epistemologies.
- This analysis is well suited to vast data bases.
- It permits researchers to grow the range of study past individual experiences.
- Amazing analysis for multiple researchers.
- Helps in interpretation of themes backed up by data.
- This analysis is applicable to even those researches which are beyond an individual’s experience.
- Allows for categories to evolve from data.
3) How to do a Thematic analysis step by step
While analyzing your research, you need to keep in mind that your methods should be as straight as possible. It is to increase the strength of your results and to make your results conclusive. There should be a visible clarity.
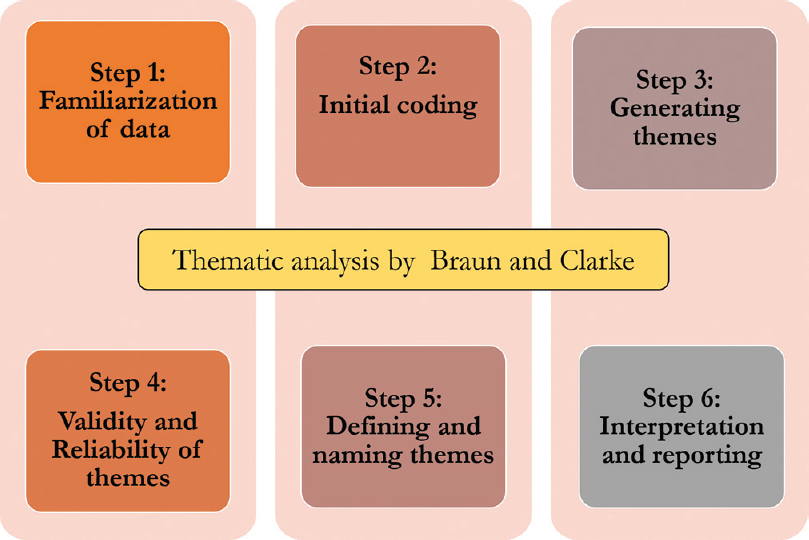
Following are the six steps of thematic analysis:
Step 1: Get familiar with your data
It is essential to get familiar with your data. Transcribe the verbal data as it is very important. Reading your data, again and again, is what will give you a brief knowledge of the data you have.
Before going on to the coding part, it is very important to actively read through your full data at least once. This stage is all about making notes on the initial ideas you have in your mind.
Step 2: Generate initial Codes
Now you can start on with initial coding for your data. Coding can be either done manually or by using a software program like NVivo. For manual coding, you can use any of the things like a highlighter, coloured pens or even post-it notes on the text which you are analyzing.
Systematic coding is what you have to do in this step. Code for as many potential themes and codes as you can. After you are done with coding, look for codes which are same and then collate them together.
Step 3: Search for themes
Well, now you must be having many codes with you. This stage is based on the broader level of themes and includes sorting the different codes into useful themes. To make it interesting, you can use visuals like mind maps, tables, etc. These are to sort your codes.
Themes are made up of different codes. Some codes may form themes or sub-themes, and then other codes may be discarded. At the end of this stage, you should be having a collection of themes and sub-themes.
Step 4: Review the themes
Now, this stage will have two levels:
- Review at the level of the coded data- Re-read all your data that fit into all your theme. It is to ensure that all your data fits accordingly. If it doesn’t work fir, then you need to give attention as your theme might not be ok and you need to re-arrange your data.
- Review at the level of the themes- Here, you need a thematic map to visualize the relationship between your themes. You need to watch, whether the themes show the meaning of your data as a whole? Keep checking till you get a satisfactory thematic map of your data.
Step 5: Define and name your themes
This step deals with the flavour of what each theme predicts and what aspect of the data each theme catch. Here, you will have an overall data. Analyze each theme and what they predict. Just check whether the themes fit into your overall data or not? Now, you should name your themes. The names should be catchy, which will attract the user and they will immediately be able to guess the theme.
After a brief analysis of the themes, now you have to produce a final thematic map. You should be able to configure each theme into few sentences to describe it.
Step 6: Produce the report
This is hence the final stage as the name itself says; it includes final write-up and report. You just have to keep in mind your audience that what type of audience are you preaching? Your report should be concise, non-repetitive, coherent and interesting. Use many examples to support your themes. This is the last step, and hence, now you will get your report.
4) Disadvantages of Thematic Analysis
- Reliability is the main concern due to large variety of interpretations from different researchers.
- Thematic analysis might miss variating data.
- It becomes difficult regarding the focus on one thing as, you get flexibility regarding analysis.
- Finding and verifying themes and codes, mix together.
- If the analysis excludes theoretical framework, then you get limited interpretive power.
- It is very difficult to maintain sense of continuity of data in each single account.
- It does not allow researchers to claim for language usage.
Conclusion:
So, I hope this article has cleared all your doubts regarding thematic analysis. I have tried to cover all the parts. If you feel that I have missed something, then kindly let me know through your valuable comments below, and I will add it to this article.
If you like this article, then do like my Blog, as I will keep coming up with more informative articles for you. For any other query regarding this article or for any online assignment help, you can email us on the id given on our website. We would love to assist you. Thank you for reading. 🙂
